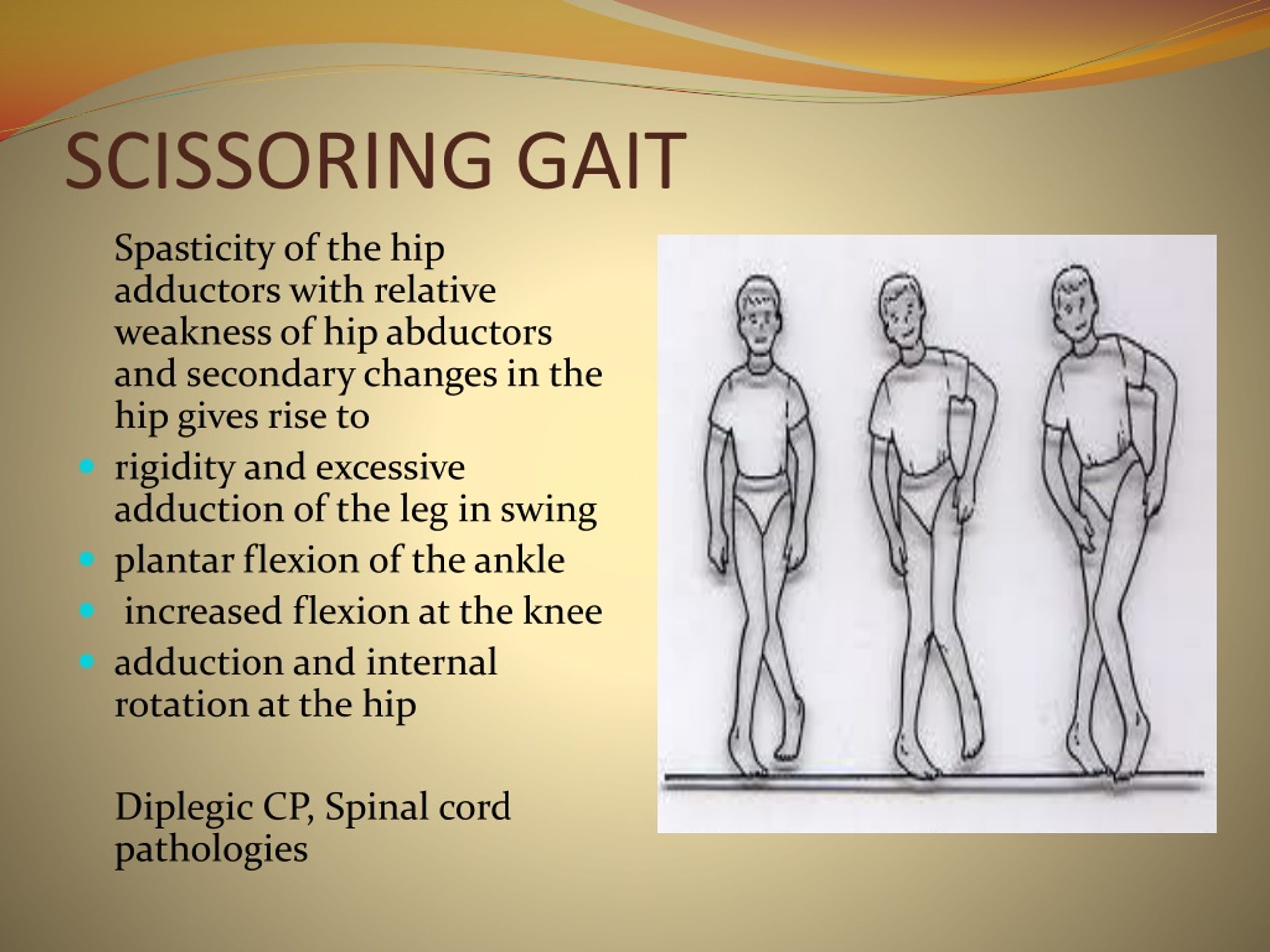
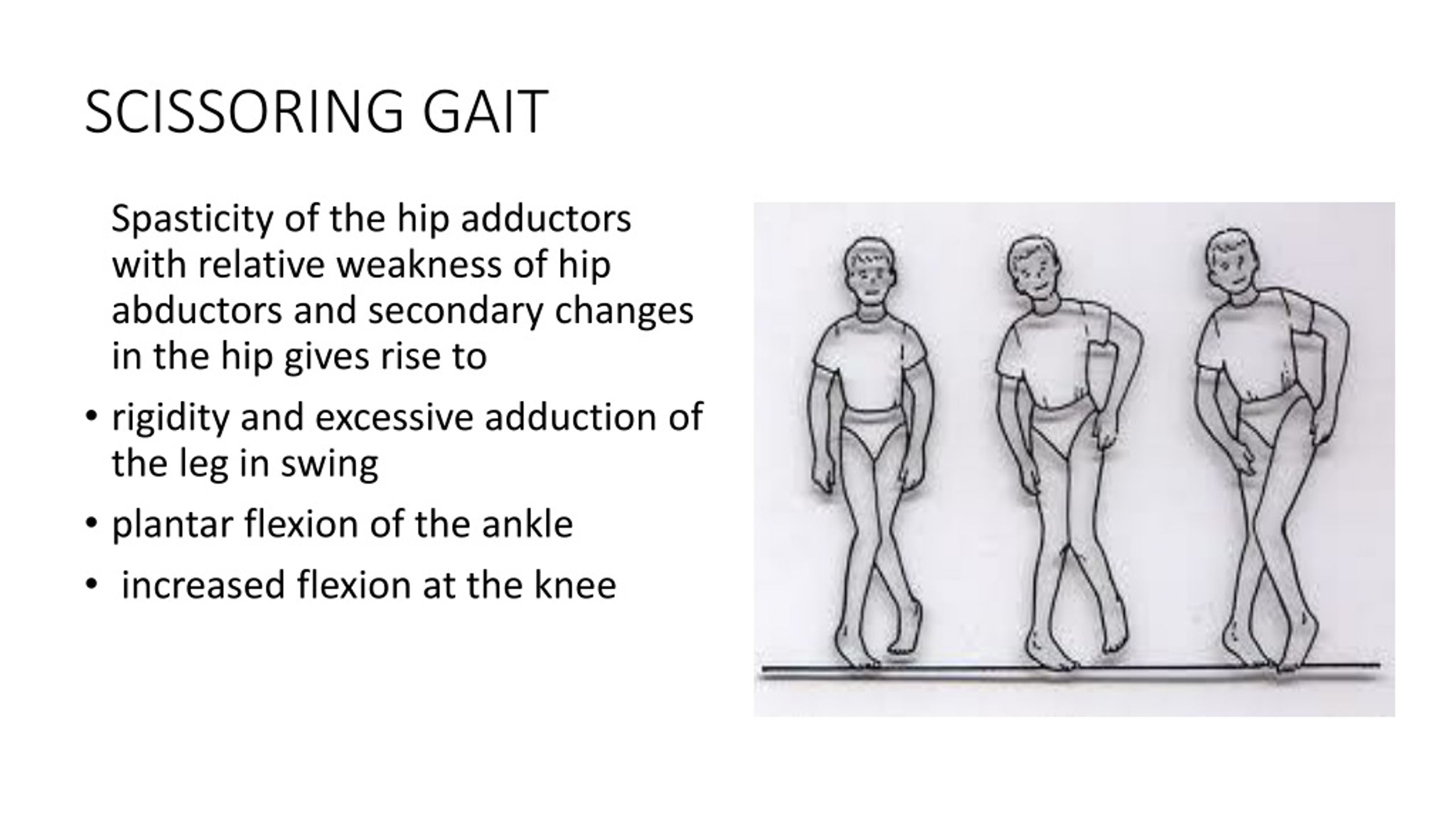
Scissoring Gait Pattern
Scissoring Gait Pattern - Stroke, or complete transection of the spinal cord). Web there is also characteristic extreme tightness of hip adductors which can cause legs to cross the midline referred to as a scissors gait. This gait pattern is reminiscent of a marionette. A scissoring gait is often a more severe form of a spastic gait. A spastic gait causes you to walk with one stiff leg. This can commonly occur with spasticity in the hip adductors. Web the best way to assess gait patterns is with gait and motion analysis. Diagnosis is made with quantitative evaluation using kinematic, kinetic and emg analysis. Scissor gait (walking with the knees turned inwards) tiptoeing (walking on the toes) crouch gait (walking with continuously bent knees, hips, and ankles) muscle weakness. Your steps may be slow and small. Another example is a scissoring gait in the absence of corticospinal tract signs (such as brisk reflexes and hip adductor spasticity). A spastic gait causes you to walk with one stiff leg. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Web gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for orthopaedic consultations in cp patients. Stroke, or complete transection of the spinal cord). Web contractures of the adductor muscles can create a ‘scissor’ type gait with a narrowed base of support. That condition and others like it are associated with an upper motor neuron lesion. This can commonly occur with spasticity in the hip adductors. This type of gait usually affects people diagnosed with spastic cerebral palsy. Diagnosis is made with quantitative evaluation using kinematic, kinetic and emg analysis. This video shows what would happen if there was no. That condition and others like it are associated with an upper motor neuron lesion. Your steps may be slow and small. Web a diplegic gait (a.k.a scissoring gait) may be caused by a lesion in the central nervous system (e.g. A scissoring gait is often a more severe form of. Web an example would be an antalgic gait in the absence of any pain or a buckling gait (knees giving way) in the presence of normal quadriceps strength. Clinical findings are similar to those in hemiplegic gait but are bilateral in nature. Cerebral palsy can make even the most basic activities, like walking or picking up a small object, difficult.. A person whose legs bend inward will often have a scissors gait. With this type, a person’s legs cross and may hit each other while walking. It is characterized by bilateral leg extension and adduction, the legs appear to be stiff. Web gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. The gait usually indicates underlying conditions, including cerebral palsy, muscle weakness, or spasticity. It is characterized by bilateral leg extension and adduction, the legs appear to be stiff. Web an example would be an antalgic gait in the absence of any pain or a buckling gait (knees giving way) in the presence of normal quadriceps strength. A scissoring gait is. Web spastic diplegic gait (scissors gait). Web there is also characteristic extreme tightness of hip adductors which can cause legs to cross the midline referred to as a scissors gait. Web contractures of the adductor muscles can create a ‘scissor’ type gait with a narrowed base of support. Web common abnormal gait patterns in individuals with spastic diplegia include: Web. Cerebral palsy can make even the most basic activities, like walking or picking up a small object, difficult. As a result of severe brain injury, some children with spastic cp also acquire secondary disorders. This video shows what would happen if there was no. Stroke, or complete transection of the spinal cord). The crisscross motion may resemble. It is characterized by bilateral leg extension and adduction, the legs appear to be stiff. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Web crouch gait is defined as excessive dorsiflexion or calcaneus at the ankle in combination with excessive flexion at the knee and hip. This can commonly occur with. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. Web many children with cerebral palsy walk with an abnormal walking pattern called scissoring gait. In countries with adequate medical care, patients with cerebral palsy may have hip adductor release surgery to minimize scissoring. Web contractures of the adductor muscles can create a. It may be accompanied by ipsilateral trunk lean with hip pain or. Web this video is a demonstration and an explanation of a scissor gait pattern. Clinical findings are similar to those in hemiplegic gait but are bilateral in nature. Web scissor gait is a form of gait abnormality primarily associated with spastic cerebral palsy. A person whose legs bend. In countries with adequate medical care, patients with cerebral palsy may have hip adductor release surgery to minimize scissoring. Treatment options include physiotherapy and medication with a muscle relaxing effect, such as baclofen and tizanidine. The gait usually indicates underlying conditions, including cerebral palsy, muscle weakness, or spasticity. Web this video is a demonstration and an explanation of a scissor. Web gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for orthopaedic consultations in cp patients. Cerebral palsy can make even the most basic activities, like walking or picking up a small object, difficult. Another example is a scissoring gait in the absence of corticospinal tract signs (such as brisk reflexes and hip adductor spasticity). A spastic gait causes you to walk with one stiff leg. Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity. To help you understand what a scissoring gait is and how it can affect your child’s future, this article will discuss its primary cause, associated risks, and various management interventions. Scissor gait (walking with the knees turned inwards) tiptoeing (walking on the toes) crouch gait (walking with continuously bent knees, hips, and ankles) muscle weakness. Web a diplegic gait (a.k.a scissoring gait) may be caused by a lesion in the central nervous system (e.g. Web spastic cp is characterized by jerky motions, muscular tightness, and joint stiffness. The gait usually indicates underlying conditions, including cerebral palsy, muscle weakness, or spasticity. Web if the muscle tone in the adductors is marked, the resulting gait disorder is referred to as scissor gait. Your steps may be slow and small. Treatment options include physiotherapy and medication with a muscle relaxing effect, such as baclofen and tizanidine. That condition and others like it are associated with an upper motor neuron lesion. Spasticity in the lower half of the legs results in plantarflexed ankles presenting in ‘tiptoe’ walking and often toe dragging. This video shows what would happen if there was no.PPT GAIT NORMAL, ABNORMAL & ASSESSMENT PowerPoint Presentation ID
Scissors Gait Techniques for Improved Mobility
Scissoring Gait and Cerebral Palsy Causes, Risks, & Treatment
Scissoring Gait
Abnormalities of Gait and Posture. Spastic Hemiparesis Scissors
Gait normal & abnormal
ABNORMAL GAIT Abnormal Gait Syndromes In general gait
Scissoring Gait
Scissoring Gait in Crouch Pattern Cerebral Palsy/Abnormal Gait
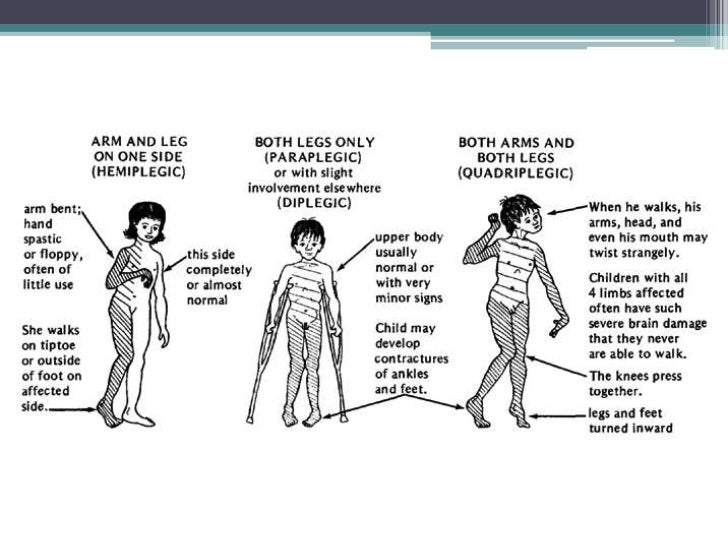
PPT CEREBRAL PALSY (CP) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web Many Children With Cerebral Palsy Walk With An Abnormal Walking Pattern Called Scissoring Gait.
Web The Best Way To Assess Gait Patterns Is With Gait And Motion Analysis.
A Scissoring Gait Is Often A More Severe Form Of A Spastic Gait.
A Scissoring Gait Is Often A More Severe Form Of A Spastic Gait.
Related Post: